Introduction to Filling Machines
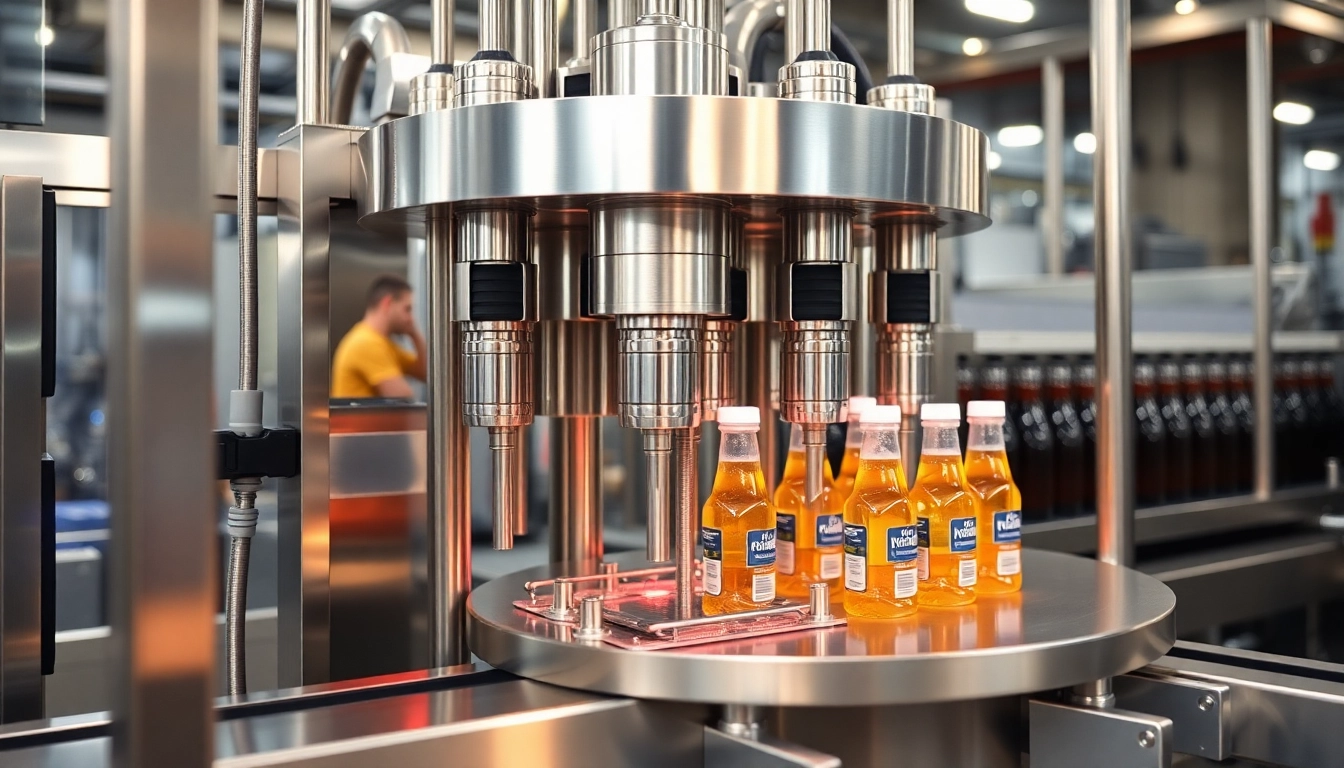
Filling machines play a critical role in the world of manufacturing and packaging. They are designed to automate the process of filling containers—be it bottles, jars, or pouches—allowing for precise measurement and increased efficiency in production lines. The evolution of filling machines has had a significant impact on various industries from food and beverage to pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. This article explores the capabilities, types, benefits, and best practices associated with filling machines, guiding manufacturers to make informed choices that optimize their operations. For those looking to explore top-rated options on filling machines in the market, check out this Filling Machine.
What is a Filling Machine?
A filling machine is a device that accurately fills containers with a specified quantity of product—liquid, powder, or even granules. These machines can range from simple manual setups to complex automated solutions. At their core, filling machines help streamline packaging processes, reduce human error, and enhance speed while maintaining consistent product quality.
Importance of Filling Machines in Manufacturing
In a manufacturing environment, efficiency is paramount. Filling machines contribute to greater throughput, allowing companies to meet high demand without compromising on quality. By automating the filling process, businesses can also free up labor for other critical tasks, thus optimizing resource allocation. Moreover, precise filling reduces waste and helps in maintaining compliance with industry standards related to packaging.
Industries Utilizing Filling Machines
Filling machines are versatile and find applications across various sectors:
- Food and Beverage: Filling machines are essential for packaging juices, sauces, dairy products, and alcoholic beverages.
- Pharmaceuticals: Precise filling is crucial for medicines in liquid and powdered forms, where dosage accuracy is vital.
- Cosmetics: Products like lotions, creams, and oils require filling machines to dispense exact amounts into containers.
- Chemicals: Industrial filling machines are used for packaging chemicals, ensuring safe and effective filling processes.
Types of Filling Machines
Manual vs. Semi-Automatic vs. Fully Automatic
Understanding the different types of filling machines is fundamental for manufacturers aiming to refine their production processes:
- Manual Filling Machines: These are the most basic type, requiring operator intervention for filling. They are ideal for small-scale operations and hobbyists.
- Semi-Automatic Filling Machines: These machines require some human input but can automate portions of the filling process. They strike a balance between efficiency and cost, making them suitable for medium-sized businesses.
- Fully Automatic Filling Machines: Designed for large-scale production, these machines can handle the entire filling process without human intervention, maximizing efficiency and minimizing labor costs.
Volumetric vs. Piston Filling Machines
Filling machines can also be categorized based on their filling mechanism:
- Volumetric Filling Machines: These machines fill containers based on predetermined volume measurements, perfect for liquid products like beverages and sauces.
- Piston Filling Machines: Utilizing cylinders and pistons, these machines are often used for thicker products such as creams, gels, or pastes, where precision is crucial.
Choosing the Right Type for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate filling machine depends on several factors including the product type, required speed, budget, and scalability. For instance, businesses looking to package highly viscous liquids should lean towards piston filling machines, while high-speed bottling lines may benefit from fully automatic volumetric machines. Assessing the specific needs of your production line will help in making the best choice.
Key Features of Modern Filling Machines
Precision and Accuracy in Filling
Modern filling machines incorporate advanced technology to ensure high precision and consistency in filling. For instance, electronic weighments and sensors allow machines to adjust in real-time, minimizing deviations and errors, which is particularly important in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals. Technology such as flow meters and load cells is commonly utilized to enhance measurement accuracy.
Automation and Efficiency Enhancements
The integration of automation technology in filling machines has revolutionized production processes. Machines are now equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that enable manufacturers to monitor and control the filling operation remotely, adjust production parameters swiftly, and maintain optimal running conditions. This increased automation enhances speed and further reduces human error during the operation.
Technical Specifications to Consider
When choosing a filling machine, it’s essential to consider the following specifications:
- Filling Speed: Measured in bottles per minute (BPM), this defines how quickly the machine can operate. A higher BPM is preferable for large production scales.
- Container Types: Different machines are designed for specific container types. Ensure compatibility with your bottles or cans.
- Material Compatibility: The machine’s construction materials should be suitable for the products being filled—e.g., food-safe materials for culinary applications.
- Cleanability: Machines that are easy to disassemble and clean help meet hygiene standards, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Benefits of Using a Filling Machine
Improved Production Rates
One of the most significant advantages of using a filling machine is the increase in production rates. Automated filling processes can significantly outperform human-driven operations, allowing businesses to meet high demand without additional labor costs. For example, a fully automated system might fill bottles at a rate of 200-600 BPM, showcasing a substantial efficiency boost compared to manual filling.
Consistency and Quality Control
With machines doing the filling, the likelihood of variations between fills is drastically reduced. Consistency is crucial in maintaining brand reputation—consumers expect the same quality and quantity with every product. Machines ensure uniformity, which is vital for compliance in industries that require precise filling standards, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Cost-Effectiveness in the Long Run
While the initial investment in filling machines might seem significant, the long-term savings speak volumes. Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes product waste due to inaccurate fills. Furthermore, downtime is reduced through continuous operation, leading to a quicker return on investment. Studies show that businesses that transition from manual to automated filling processes can see a 20-30% reduction in their overall operational costs over time.
Best Practices for Operating Filling Machines
Regular Maintenance and Troubleshooting
To ensure optimal performance and longevity, regular maintenance of filling machines is essential. Here are key maintenance tips:
- Routine Checks: Schedule routine inspections for wear and tear, and replace parts as needed to avoid breakdowns.
- Calibration: Periodically calibrate the filling machine to confirm it is dispensing the correct amount.
- Cleaning: Maintain hygiene by routinely cleaning the machine, especially if used for food products.
Training and Safety Procedures for Operators
Even with automation, skilled operators are crucial for overseeing the filling process. Providing comprehensive training ensures that operators are well-versed in operating procedures, emergency protocols, and safety measures. Establishing a culture of safety not only protects workers but also minimizes the risk of errors that could lead to product recalls.
Innovations in Filling Technology
As technology advances, new innovations in filling machine design have emerged, enhancing efficiency and adaptability. Examples include:
- Smart Technologies: IoT-enabled machines provide real-time analytics and monitoring for decision-making improvements.
- Flexible Systems: Modular machines can be easily reconfigured for different products or container types, accommodating diverse production needs.
- Sustainability Features: Machines designed for minimal waste and energy consumption meet the growing demand for environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
Conclusion
Filling machines are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, capable of enhancing efficiency, consistency, and quality for a variety of industries. Understanding the types and benefits of these machines empowers businesses to make informed choices that propel their operations forward. Regular maintenance, operator training, and keeping abreast of technological innovations will further optimize the performance of filling machines, solidifying their role in the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing.